Lesson 11.2 identifying arrhythmia patterns – Lesson 11.2: Identifying Arrhythmia Patterns delves into the captivating world of cardiac arrhythmias, providing an in-depth exploration of their diverse patterns, diagnostic techniques, and clinical significance. This comprehensive guide equips readers with the knowledge and skills necessary to accurately identify and manage these potentially life-threatening conditions.
Arrhythmias, deviations from the heart’s normal electrical rhythm, manifest in a myriad of patterns, each with its own unique set of characteristics. Understanding these patterns is paramount for effective diagnosis and treatment, as they provide valuable insights into the underlying causes and potential consequences of arrhythmias.
Arrhythmia Patterns

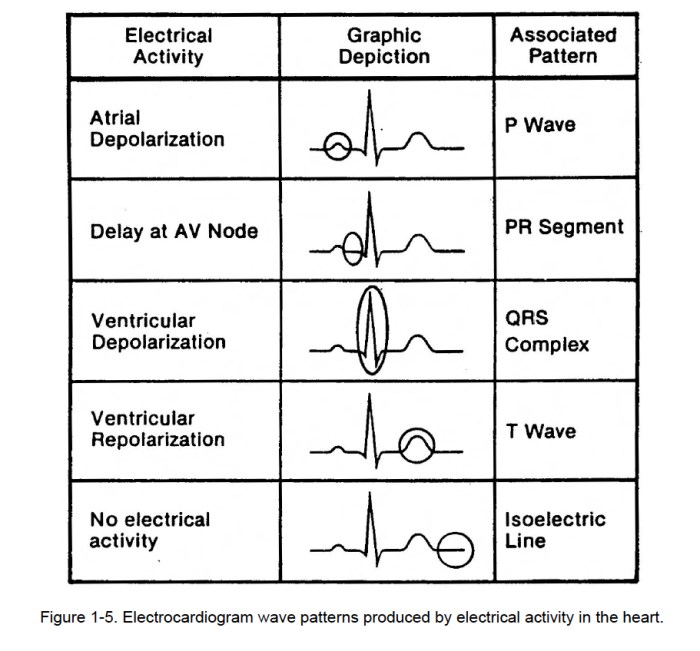
Arrhythmias are abnormalities in the heart’s electrical conduction system, which can lead to irregular heartbeats. These irregular heartbeats can be classified into different patterns based on their characteristics.
Types of Arrhythmia Patterns
- Tachyarrhythmias:Heart rates above 100 beats per minute (bpm)
- Bradyarrhythmias:Heart rates below 60 bpm
- Conduction abnormalities:Problems with the electrical signals traveling through the heart
- Extrasystoles:Premature heartbeats that occur before the next expected beat
Each type of arrhythmia pattern has its own unique characteristics and causes.
Causes of Arrhythmia Patterns
- Coronary artery disease
- Heart failure
- Electrolyte imbalances
- Thyroid disorders
- Medications
- Caffeine and alcohol
Identifying Arrhythmia Patterns
Arrhythmia patterns can be identified using various methods, including:
Methods Used to Identify Arrhythmia Patterns
- Electrocardiography (ECG)
- Holter monitoring
- Event recorders
- Implantable loop recorders
ECG is the most commonly used method, which involves placing electrodes on the chest to record the heart’s electrical activity. Accurate arrhythmia pattern identification is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Challenges Associated with Arrhythmia Pattern Identification
- Intermittent nature of arrhythmias
- Similar patterns between different arrhythmias
- Noise and artifacts in recordings
Clinical Significance of Arrhythmia Patterns: Lesson 11.2 Identifying Arrhythmia Patterns
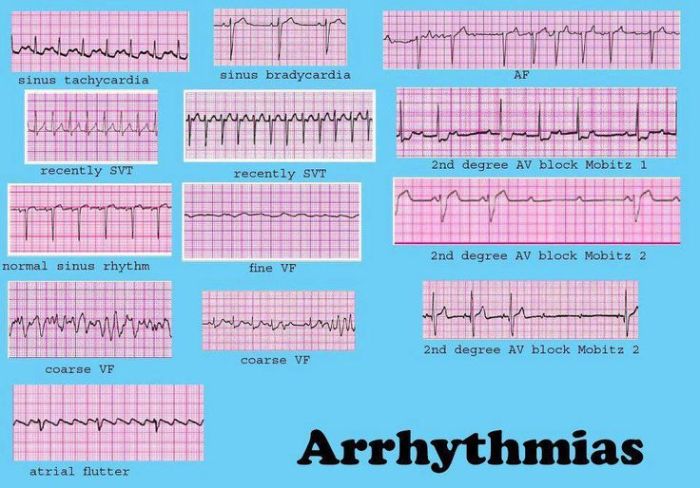
Arrhythmia patterns can have significant clinical implications, including:
Clinical Significance of Arrhythmia Patterns, Lesson 11.2 identifying arrhythmia patterns
- Increased risk of stroke, heart attack, and sudden cardiac death
- Palpitations, chest pain, and shortness of breath
- Impaired cardiac function
Understanding arrhythmia patterns is essential for appropriate patient care and treatment decisions.
Management of Arrhythmia Patterns
Management of arrhythmia patterns depends on the type and severity of the arrhythmia. Approaches may include:
Different Approaches to Managing Arrhythmia Patterns
- Medications:To control heart rate, rhythm, and prevent blood clots
- Catheter ablation:A procedure to destroy small areas of heart tissue causing arrhythmias
- Pacemakers and implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs):Devices to regulate heart rate and prevent sudden cardiac death
- Lifestyle modifications:Such as quitting smoking, reducing alcohol intake, and managing stress
The efficacy and safety of different arrhythmia management strategies vary depending on the individual patient and the specific arrhythmia pattern.
Commonly Asked Questions
What are the most common types of arrhythmia patterns?
The most common types of arrhythmia patterns include sinus arrhythmia, atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, ventricular tachycardia, and ventricular fibrillation.
How are arrhythmia patterns identified?
Arrhythmia patterns are typically identified using electrocardiography (ECG), which records the electrical activity of the heart.
What is the clinical significance of arrhythmia patterns?
Arrhythmia patterns can provide valuable information about the underlying heart condition, the severity of the arrhythmia, and the potential risk of complications.