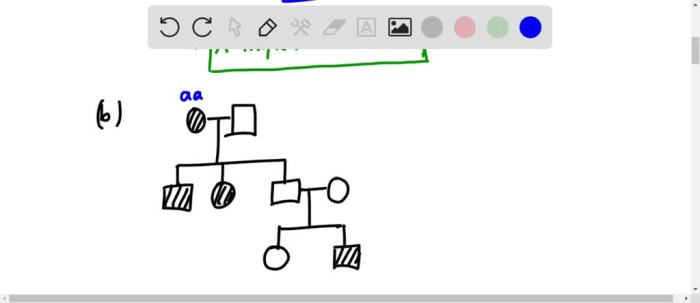
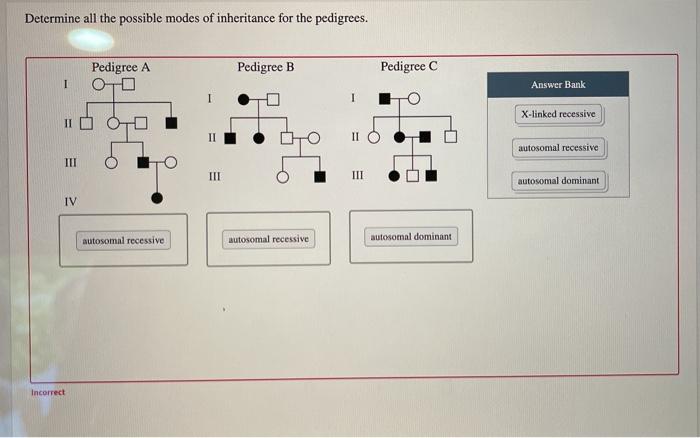
Determine all the possible modes of inheritance for the pedigrees sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of pedigree analysis, empowering individuals with the knowledge to decipher the patterns of inheritance within families and unravel the mysteries of genetic traits.
Modes of Inheritance
Modes of inheritance refer to the different patterns in which genetic traits are passed from parents to offspring. These patterns are determined by the location of the genes responsible for the trait on the chromosomes and the nature of the alleles involved.
The two main types of inheritance patterns are dominant and recessive inheritance.
Dominant Inheritance
In dominant inheritance, the allele for the dominant trait masks the effect of the allele for the recessive trait. This means that even if an individual carries only one copy of the dominant allele, they will still express the dominant trait.
Examples of dominant traits include brown eyes, dark hair, and tall stature.
Recessive Inheritance, Determine all the possible modes of inheritance for the pedigrees
In recessive inheritance, the allele for the recessive trait is only expressed when an individual carries two copies of the allele. If an individual carries only one copy of the recessive allele, they will be a carrier for the trait but will not express it.
Examples of recessive traits include blue eyes, red hair, and cystic fibrosis.
Homozygous and Heterozygous Genotypes
The genotype of an individual refers to the combination of alleles they carry for a particular gene. Individuals who carry two identical alleles for a gene are said to be homozygous for that gene. Individuals who carry two different alleles for a gene are said to be heterozygous for that gene.
For example, an individual who carries two copies of the dominant allele for brown eyes is homozygous for eye color. An individual who carries one copy of the dominant allele and one copy of the recessive allele for eye color is heterozygous for eye color.
Modes of Inheritance Table
| Mode of Inheritance | Example | Genotype | Phenotype |
|---|---|---|---|
| Autosomal Dominant | Brown eyes | BB or Bb | Brown eyes |
| Autosomal Recessive | Cystic fibrosis | cc | Cystic fibrosis |
| X-Linked Dominant | Red-green colorblindness | X^C X^C or X^C X^c | Red-green colorblind |
| X-Linked Recessive | Hemophilia | X^h X^h | Hemophiliac |
Pedigree Analysis
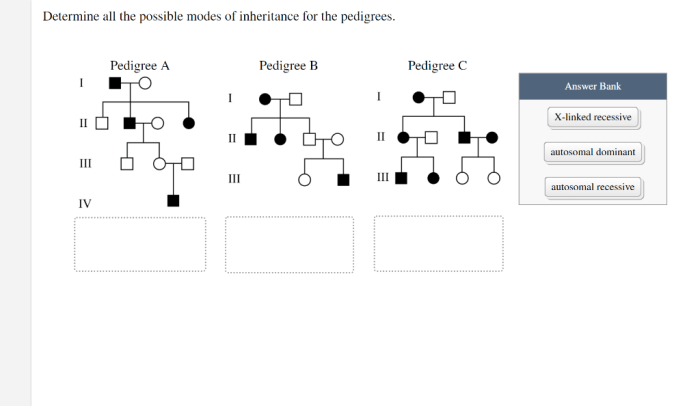
Pedigree analysis is a method used to trace the inheritance of traits through multiple generations of a family. Pedigrees are diagrams that use symbols to represent individuals and their relationships, and they can be used to identify patterns of inheritance and to determine the mode of inheritance for a particular trait.
To analyze a pedigree, the following steps are typically followed:
- Identify the affected individuals.
- Determine the mode of inheritance.
- Identify the carriers.
Pedigree analysis can be used to identify carriers of genetic disorders, which is important for genetic counseling and family planning. It can also be used to identify at-risk individuals for genetic disorders, which can lead to early intervention and treatment.
Flowchart of Pedigree Analysis
Start
Identify the affected individuals
Determine the mode of inheritance
Identify the carriers
End
Applications of Pedigree Analysis: Determine All The Possible Modes Of Inheritance For The Pedigrees
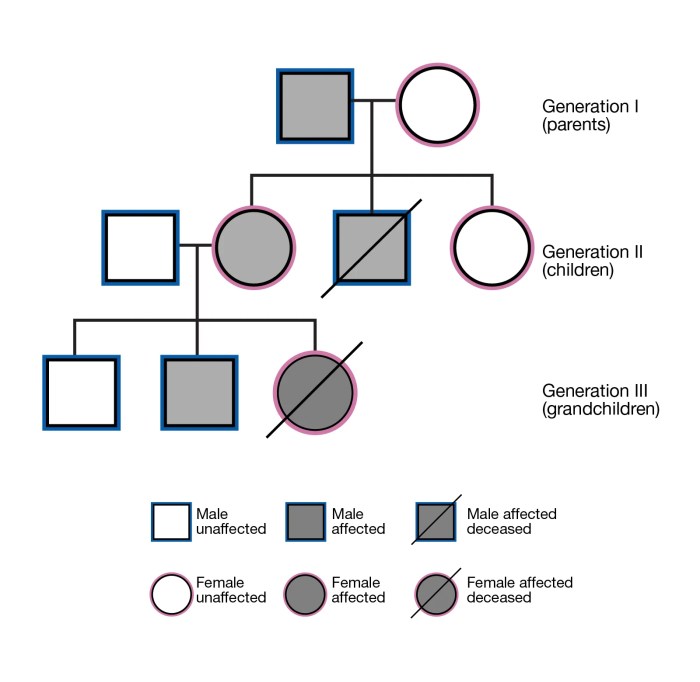
Pedigree analysis has a wide range of applications in genetic counseling and medicine. Some of the most common applications include:
- Identifying carriers of genetic disorders
- Identifying at-risk individuals for genetic disorders
- Studying the inheritance of complex traits
- Providing genetic counseling to families
Pedigree analysis is a valuable tool for understanding the inheritance of genetic traits and for identifying individuals who are at risk for genetic disorders.
Limitations of Pedigree Analysis
Pedigree analysis is a powerful tool, but it does have some limitations. These limitations include:
- Incomplete or inaccurate information
- Environmental factors
- Genetic testing
Incomplete or inaccurate information can lead to incorrect conclusions about the mode of inheritance for a particular trait. Environmental factors can also affect the expression of genetic traits, which can make it difficult to determine the mode of inheritance.
Genetic testing can be used to complement pedigree analysis and to provide more accurate information about the inheritance of a particular trait.
FAQs
What is pedigree analysis?
Pedigree analysis is a method of studying the inheritance of traits within a family by constructing a diagram that represents the relationships between family members and the occurrence of a particular trait.
What are the different modes of inheritance?
The main modes of inheritance are autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, X-linked dominant, and X-linked recessive.
How can pedigree analysis be used in genetic counseling?
Pedigree analysis can be used in genetic counseling to assess the risk of inherited disorders and to provide information about the inheritance patterns of specific traits.